
Problems playing this file? See media help. A piece in 3Ĩ, simply by halving the length of the notes. In a sense, all simple triple time signatures, such as 3Ģ, etc.-and all compound duple times, such as 6ġ6 and so on, are equivalent. On a formal mathematical level, the time signatures of, e.g., 3Ĩ are interchangeable.

Correspondingly, at slow tempos, the beat indicated by the time signature could in actual performance be divided into smaller units. For example, a fast waltz, notated in 3Ĥ time, may be described as being one in a bar. To the ear, a bar may seem like one singular beat. Terms such as quadruple (4), quintuple (5), and so on, are also occasionally used. Time signatures indicating two beats per bar (whether in simple or compound meter) are called duple meter, while those with three beats to the bar are triple meter.

The rhythm of actual music is typically not as regular. These examples assume, for simplicity, that continuous eighth notes are the prevailing note values. It is felt asĨ comprises not three groups of two eighth notes (quavers) but two groups of three eighth-note (quaver) subdivisions. In the examples below, bold denotes a more-stressed beat, and italics denotes a less-stressed beat.Ĥ is a simple triple meter time signature that represents three quarter notes (crotchets). The lower number is most commonly an 8 (an eighth-note or quaver): as in 9
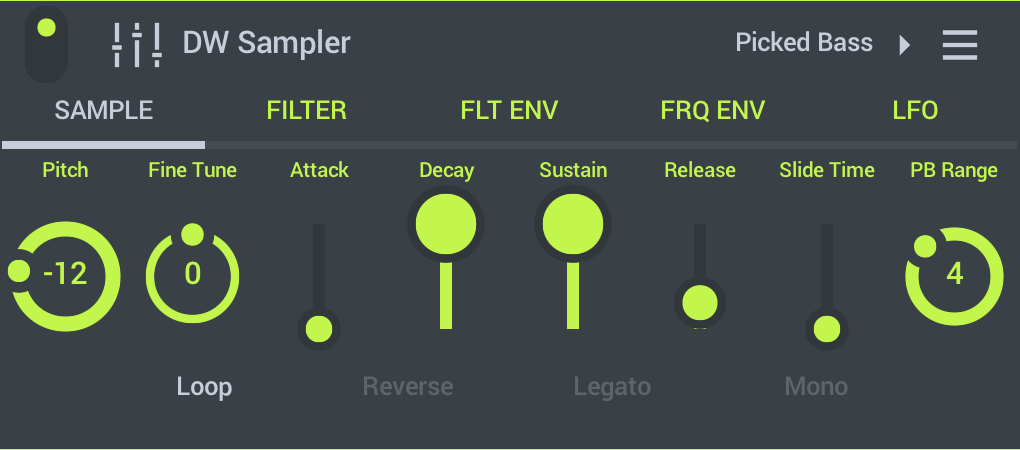
The upper numeral of compound time signatures is commonly 6, 9, or 12 (multiples of 3 in each beat). In compound meter, subdivisions (which are what the upper number represents in these meters) of the beat are in three equal parts, so that a dotted note (half again longer than a regular note) becomes the beat. In modern notation, it is used in place of 2Ģ and is called alla breve or, colloquially, cut time or cut common time.
#Glissando slide fl studio sakura full
The symbol is derived from a broken circle used in music notation from the 14th through 16th centuries, where a full circle represented what today would be written in 3Ĥ time and was called tempus perfectum (perfect time). The most common simple time signatures are 2īy convention, two special symbols are sometimes used for 4Ĥ time, also called common time or imperfect time.
The time signature (also known as meter signature, metre signature, or measure signature) is a notational convention used in Western musical notation to specify how many beats (pulses) are contained in each measure ( bar), and which note value is equivalent to a beat. The time signature indicates that there are three quarter notes (crotchets) per measure (bar).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
